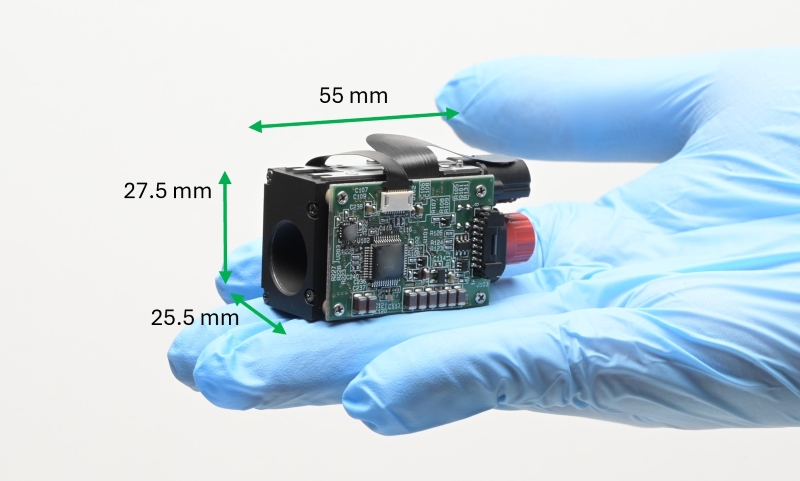
TAMRON Beam Divergence Control Module
Optical Device for Free Space Optical Communication - "Beam Divergence Control Module"
High-precision beam control technology
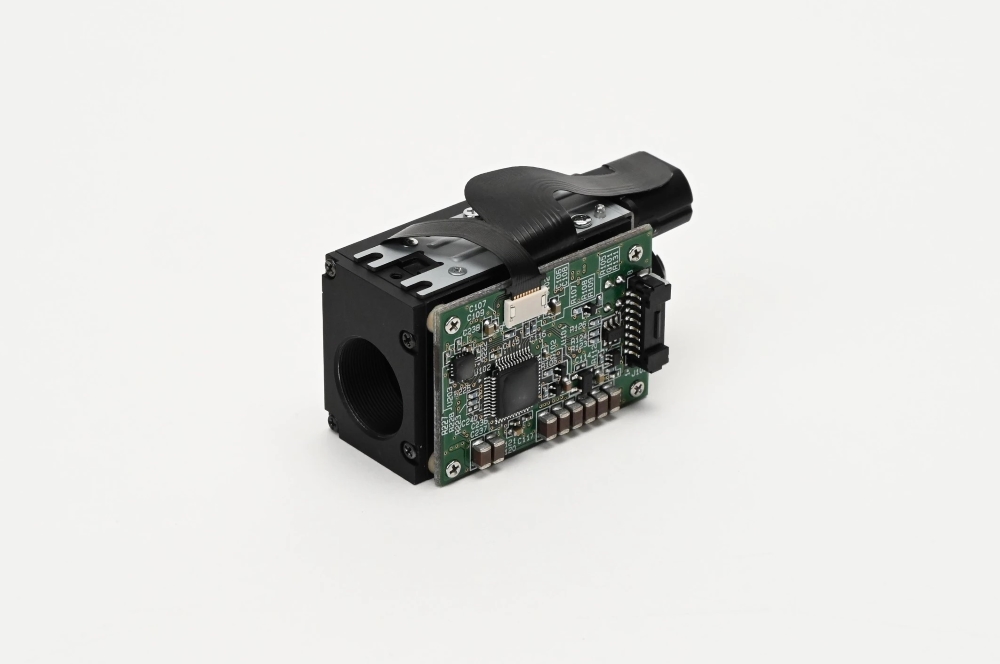
The Beam Divergence Control (BDC) module is an optical device designed for laser communication terminals. By optimally varying the beam divergence angle through the movement of the built-in lens, it enhances the efficiency of the PAT (Pointing, Acquisition, Tracking) process in free space optical (FSO) communication. This product was developed as a prototype in collaboration with the National Institute of Information and Communications Technology (NICT), and our company has successfully achieved miniaturization and space compatibility.

Features
The beam divergence angle is controlled in real-time to achieve the optimal angle based on the communication distance and error, thereby contributing to the high efficiency of the PAT process.
By utilizing photographic zoom lens technology, we have developed a high-precision lens drive system that operates effectively in a space environment.
Designed for integration into LCT, our system achieves low SWaP (Size, Weight, and Power Consumption).
NTN (Non-Terrestrial Network) and FSO
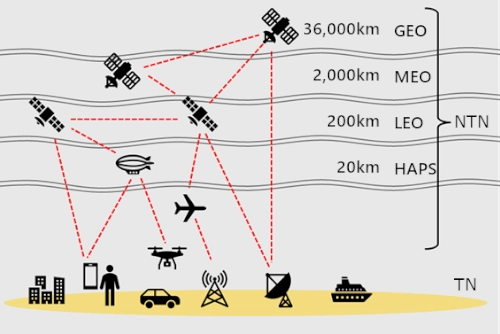
NTN (Non-Terrestrial Network) refers to a network that utilizes satellites and unmanned aerial vehicles to create a multi-layered connection from space to the ground, with ongoing technological development aimed at the Beyond 5G/6G era. In this effort to establish NTN, there is growing attention on free space optical (FSO) communication technology. This technology enables high-speed, large-capacity communication compared to conventional RF communication and offers enhanced information confidentiality due to the use of highly directional beams. Particularly in inter-satellite optical communication, the PAT (Pointing, Acquisition, Tracking) process, which involves high-precision alignment for establishing communication links between distant satellites, is crucial and is performed by a laser communication terminal (LCT).
Function of BDC within the LCT
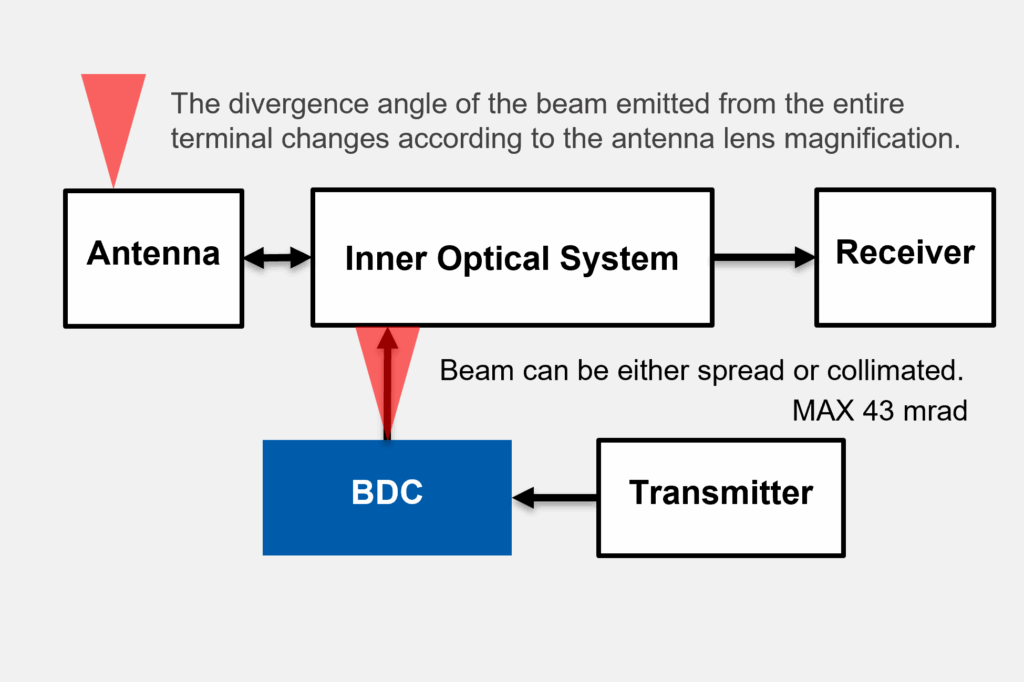
The transmitting beam, with its beam divergence angle adjusted through the BDC module, enters the internal optical system.
Examples of applications
Utilization in the PAT Process
Currently, standardization of FSO communication is underway. The U.S. SDA standard* has adopted a beaconless PAT process that utilizes the transmitting beam instead of a beacon beam. By employing the BDC, it becomes possible to adjust the beam divergence angle to the optimal level based on the uncertainty of the receiving satellite’s position, thereby enhancing the efficiency of the PAT process.
*SDA standard: A standard for optical satellite communication established by the U.S. Space Development Agency.

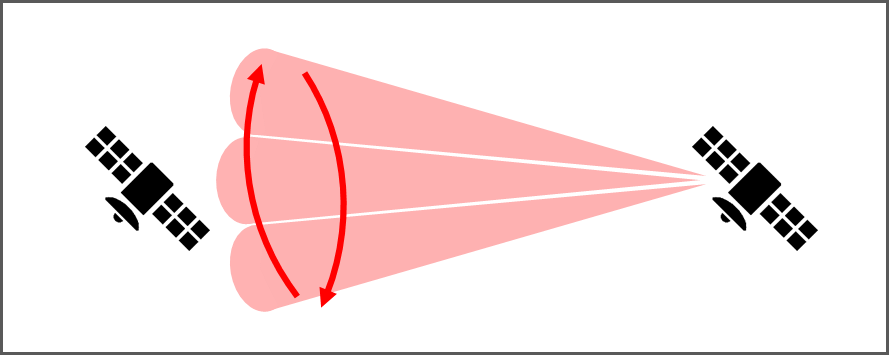
Scanning Method Using Collimated Beam (Without BDC)
This is a representative method of the PAT process for inter-satellite optical communication. It establishes links between satellites using highly directional communication beam without the use of beacon beam.
Utilization During Transmitting
Scanning Method Using Divergent Beam (With BDC)
By using the BDC, the PAT process can be performed at the optimal beam divergence angle, which is expected to enhance the efficiency of the PAT process.

During transmitting, the beam divergence angle can be adjusted to the optimal level with minimal data loss, according to the distance and antenna aperture of the receiving satellite.
Functions
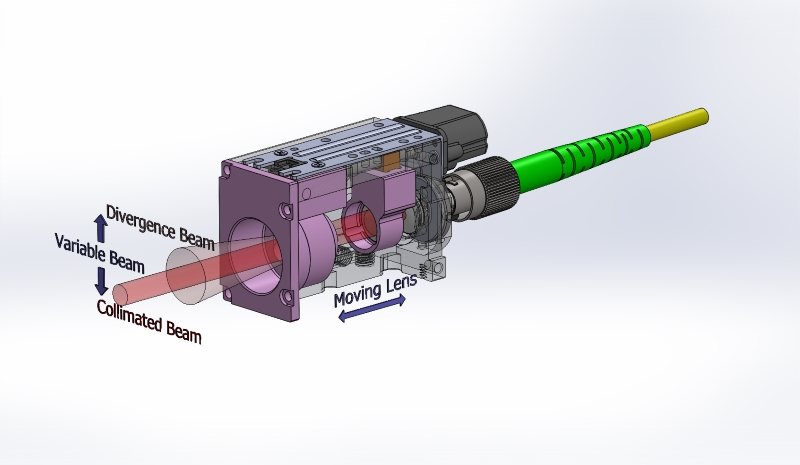
With our developed actuators and control system, the beam divergence angle can be continuously adjusted from collimated beam to a maximum of 43 mrad.
Specifications
| Size | W 25.5 × H 27.5 × D 55mm (including the substrate) | |
| Weight | 52g (Approx.) | |
| Collimated Size / Divergence Angle | Φ2.0mm / 964μrad | |
| Variable Angle | Collimated beam to 43mrad | |
| Power Consumption | 0.6W | |
| Connector Type | FC/APC | |
| Wavelength Band | C Band (1530~1565nm) | |